Fertilizing is the secret to lush, colorful flower beds. Whether you’re cultivating annuals, perennials, or mixed borders, the right fertilization approach ensures strong roots, abundant blooms, and healthy soil that sustains your garden year after year.
Many gardeners wonder why their flower beds don’t produce the spectacular displays they envision, and the answer often lies in proper nutrition.
This complete guide explains how to fertilize flower beds step-by-step – including timing, techniques, and expert tips to help your garden thrive from spring through fall.
What is a flower fertilizer?
Unlike general-purpose fertilizers, flower fertilizers emphasize the nutrients that drive bloom production and plant vitality. The foundation includes the 3 key macronutrients, represented as N-P-K: Nitrogen, Phosphorus, and Potassium.
What each nutrient does
Understanding the role of each primary nutrient helps you choose the right fertilizer for your specific flower bed needs.
- Nitrogen (N) stimulates green leafy growth, promoting lush foliage and overall plant vigor. Too much nitrogen can result in all leaves and no flowers.
- Phosphorus (P) is the bloom booster. This nutrient encourages robust root development and, most importantly, flower production.
- Potassium (K) strengthens stems and enhances overall plant resistance to disease, pests, and environmental stress. Think of potassium as your flower bed’s immune system supporter, helping plants withstand heat, drought, and other challenging conditions.
Common types of flower fertilizer
Choosing the right fertilizer type depends on your gardening style, the plants you’re growing, and how hands-on you want to be with feeding.
Granular fertilizer
Granular fertilizer offers ease of application and provides long-lasting nutrient release. Simply scatter the granules around your plants, water them in, and they’ll continue feeding your flowers for weeks. This type works well for busy gardeners who want effective results without constant attention.
Liquid fertilizer
Liquid fertilizer provides fast-acting nutrition for quick absorption. When your plants need an immediate boost or you notice signs of nutrient deficiency, liquid formulas deliver nutrients directly to roots through watering. They’re perfect for container gardens and hanging baskets that need frequent feeding.
Slow-release pellets
Slow-release pellets are ideal for consistent feeding over several months. These specialized formulations gradually break down, releasing nutrients steadily throughout the growing season. One application in spring can often carry your flower beds through summer.
Organic options
Organic options like compost, worm castings, bone meal, or fish emulsion support sustainable gardening practices while improving long-term soil health.
These natural amendments not only feed your plants but also enhance soil structure, encourage beneficial microorganisms, and create a thriving underground ecosystem.
How to fertilize flower beds (step-by-step guide)
Successfully fertilizing flower beds involves more than just sprinkling products around your plants. Follow these steps for optimal results.
Step 1: Test your soil first
Before adding any fertilizer, understand what your soil already contains.
Use a soil test kit available at most garden centers to check pH levels and existing nutrient concentrations. Most flowering plants prefer slightly acidic to neutral soil with a pH between 6.0 and 7.0.
Testing eliminates guesswork and prevents over-application of nutrients your soil may already have in abundance. Your local cooperative extension office often provides affordable soil testing services with detailed recommendations.
Step 2: Choose the right fertilizer formula
Different flowering plants have different nutritional needs throughout their lifecycles.
- For annuals that bloom throughout the season, select a higher phosphorus formula such as 10-20-10. This promotes prolific flower production, which is exactly what you want from petunias, marigolds, and impatiens.
- Perennials benefit from a balanced blend like 10-10-10 that supports steady, sustainable growth year after year. Since these plants invest energy in root establishment and longevity, they need well-rounded nutrition rather than an exclusive bloom focus.
- Flowering shrubs thrive with slow-release organic options that provide sustained feeding without the risk of nutrient burn. Roses, hydrangeas, and azaleas particularly appreciate gentle, consistent nutrition.
Step 3: Prepare the flower bed
Proper preparation ensures your fertilizer works effectively.
- Begin by removing any weeds that would compete with your flowers for nutrients.
- Gently loosen compacted soil with a hand cultivator or garden fork to improve nutrient penetration.
- Water your flower bed lightly before applying fertilizer. This crucial step moistens the soil and helps prevent root burn from concentrated fertilizer contact.
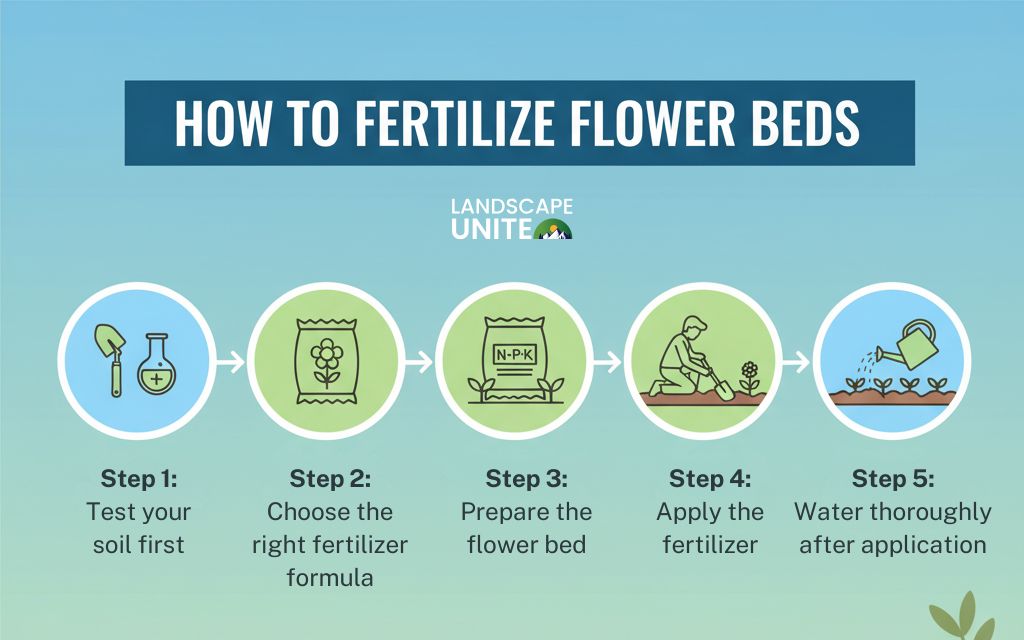
Step 4: Apply the fertilizer
Application technique varies depending on the fertilizer type you’ve chosen.
- For granular fertilizer, scatter the product evenly around each plant, maintaining a 2 to 3-inch distance from stems and crown areas. This spacing prevents direct contact that could damage plant tissue. Use the amount recommended on the package – more is not better when it comes to fertilization.
- Liquid fertilizer should be diluted according to label instructions and applied directly to the soil near the base of plants. Avoid splashing leaves, as this can cause burning. Pour slowly and evenly to ensure the solution reaches the root zone where it’s needed most.
- Slow-release pellets require gentle incorporation into the top inch of soil. Lightly scratch them into the surface around your plants, then water thoroughly. As these pellets gradually break down, they’ll release nutrients consistently over time.
Step 5: Water thoroughly after application
Regardless of which fertilizer type you use, always water thoroughly after application.
This critical step helps nutrients dissolve and soak into the soil, carrying them down to plant roots where they can be absorbed effectively.
Watering also prevents fertilizer from sitting on the soil surface where it can volatilize or wash away during the next rain.
Why should you fertilize flower beds?
Boosts bloom production
Flower fertilizer provides the essential nutrients that drive abundant, longer-lasting flower production. Phosphorus and potassium work together to trigger bloom development, increase flower size, and extend the blooming period.
Without adequate nutrition, even healthy-looking plants may produce disappointing displays.
Strengthens root and leaf growth
Balanced feeding supports strong stem development and lush foliage, preventing weak or leggy plants that flop over or break in wind and rain.
Strong roots establish quickly, anchor plants, and improve drought resistance. Healthy foliage photosynthesizes efficiently, generating the energy plants need for spectacular blooms.
Improves Soil Health Over Time
Regular fertilization replenishes nutrients that are depleted by frequent watering, dense plantings, and continuous plant growth. Especially when using organic fertilizers, you’re not just feeding plants – you’re building better soil structure, encouraging beneficial microbial activity, and creating a sustainable ecosystem for your flowers.
When to fertilize flower beds
Early spring
As soil temperatures warm and plants emerge from dormancy, apply fertilizer to jumpstart new growth before the blooming season begins. This early feeding gives plants the nutritional foundation they need to develop strong stems, healthy foliage, and abundant flower buds. For most US regions, early to mid-spring (March through April) is ideal.
Mid-summer
Reapply fertilizer in mid-summer to sustain flowering throughout the peak growing season. By July, spring-applied nutrients have been depleted, and plants benefit tremendously from supplemental feeding.
Late fall (Optional)
For perennials and flowering shrubs, consider applying a gentle organic fertilizer in late fall to strengthen roots before winter dormancy. This optional feeding helps plants store energy reserves and promotes emergence the following spring.
Avoid high-nitrogen fertilizers at this time, which could stimulate tender new growth vulnerable to frost damage.

How often to fertilize flower beds
Frequency depends on plant type, fertilizer formulation, and growing conditions.
- Annual flowers require feeding every 4 to 6 weeks during their active growth period. These bloomers consume nutrients rapidly and need replenishment to maintain their impressive floral displays from spring through frost.
- Perennials need fertilization just once in spring and again at mid-season. Their slower growth rate and focus on long-term root establishment mean they don’t require the frequent feeding that annuals do.
- Newly planted beds need special consideration. Wait 4 to 6 weeks after planting before the first feeding to allow roots to establish without the stress of concentrated nutrients. Young transplants are sensitive and can suffer from fertilizer burn if fed too soon.
Remember this crucial principle: Avoid over-fertilizing.
Too much nitrogen produces lush leaves but fewer flowers, defeating the purpose of fertilizing a flower bed. Always follow package directions and observe how your plants respond before increasing application rates.
Tips for sustainable fertilizing
- Use organic flower fertilizer whenever possible to improve soil life and long-term health.
- Compost regularly to reduce dependency on synthetic fertilizers.
- Avoid fertilizer runoff by never applying before heavy rain. Excess nutrients washing into storm drains contribute to water pollution and represent wasted money and effort.
- Check the forecast and time applications for dry periods followed by gentle watering.
- Rotate plant types seasonally to balance nutrient use across your beds. Different plants have different nutritional needs, and rotation helps prevent soil depletion of specific nutrients.
Conclusion
Fertilizing flower beds is simple once you know what your plants need and when to feed them. Start by testing your soil, choose the appropriate fertilizer for your specific flowers, and follow the step-by-step application process outlined in this guide.
Pay attention to timing – spring for growth, summer for sustained blooms, and fall for root strengthening – and you’ll see remarkable improvements in both flower quantity and quality.
Check out more helpful flower bed guides in our gardening library to continue building your expertise and creating the stunning landscape you envision!
Frequently asked questions (FAQs)
What is the best fertilizer for flower beds?
A balanced or bloom-boosting fertilizer like 10-20-10 works best for most flowering plants. The higher phosphorus content (the middle number) promotes abundant flower production.
When should I fertilize my flower beds?
Apply fertilizer in early spring to support new growth, mid-summer to sustain blooms throughout the peak season, and lightly in fall to strengthen root health before winter dormancy. Timing applications to match plant growth cycles maximizes effectiveness.
Should I fertilize before or after watering?
Water lightly before applying fertilizer and then water thoroughly afterward. The initial watering moistens the soil and prevents root burn, while post-application watering helps nutrients dissolve and penetrate down to the root zone where plants can absorb them.
How do I know if my flower beds need fertilizer?
Watch for signs including yellowing leaves (especially lower leaves), slow or stunted growth, fewer blooms than usual, or weak stems that flop over easily. However, don’t wait for problems to appear – proactive fertilization based on the schedule outlined in this guide prevents deficiencies.
Can I use vegetable or lawn fertilizer for flowers?
This isn’t recommended. Flower fertilizers have specific phosphorus ratios that promote blooming rather than just leafy growth. Lawn fertilizers are high in nitrogen, which encourages grass blade growth but can actually reduce flower production in ornamentals. Always choose fertilizers formulated specifically for flowering plants to get the best results.


